Fundamental requirements of masonry pdf
While the fundamental principles of designing reinforced masonry structures discussed in the first edition (2001) of this book remain valid, revisions in codes, specifications, and reference standards applicable to design and construction of masonry structures that have since occurred required updating that book in the form of this second edition.
BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR CONCRETE MASONRY TEK 1-3D Codes & Specs (2011) INTRODUCTION The majority of jurisdictions in the United States adopt a national model code, most commonly the International Building Code (IBC) (refs. 1, 2), as the basis of their building code. The intent of the IBC is to reference and coordinate other standardized documents, rather than to develop …
The Definitive Guide to Designing Reinforced Masonry Structures Fully updated to the 2009 International Building Code (2009 IBC) and the 2008 Masonry Standards Joint Committee (MSJC-08), Design of Reinforced Masonry Structures, second edition, presents the latest methods for designing strong, safe, and economical structures with reinforced masonry.
Masonry Fundamentals. Masonry is the trade which historically has been fundamental to all construction. Without a mason there would be no foundations or buildings.
Masonry design standards throughout the world generally give the performance requirements in a ‘high level’ way, without spelling out in full detail the ways in which those requirements must be satisfied.
Wall Ties and Restraint Fixings Type A ties must have a measured dynamic stiffness of <4.8MN/m3 for the specified minimum cavity, at a standard density.
Masonry structures are required to be designed in accordance with the general rules given in Eurocode, which requires that: Ed ≤ Rd where Ed = design value of the effect of actions Rd = design value of the resistance The basic requirements of Section 2 of Eurocode are deemed to be satisfied for masonry structures when the following are applicable: Limit state design in conjunction with the
2.1 Building Code Requirements For Masonry Structures (ACI 530-02/ASCE 5-02/TMS 402-02) This code is produced by the joint efforts of American Concrete Institute, the Structural Engineering Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers and The Masonry Society. The Code covers the design and construction of masonry structures and is accompanied with a Commentary on the Building code
REQUIREMENTS OF THE MASONRY STANDARD Although not explicitly stated therein, AS 3700 Masonry Structuresassumes that the characteristic tensile flexural bond strength will be not less than
Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures, TMS 402/ACI 530/ASCE 5. IBC International Code Council. 2009. International Building Code. NCMA National Concrete Masonry Association. A Manual of Facts on Concrete Masonry, NCMA-TEK is an information series from the National Concrete Masonry Association, various dates. NCMA-TEK 14-1BA, Section Properties of Concrete Masonry …
It includes the requirements for ensuring that the planning, preparing, initiating, monitoring, adjusting and reporting of civil masonry, crib and gabion structure construction tasks are carried out in accordance with the accepted industry principles.
530.1R-02 Commentary on Specification for Masonry Structures

1. Introduction to Eurocode 6
GUIDE TO STANDARDS & TOLERANCES 2007 04 cOntEnts (CONT) ITEM TOPIC PAGE 3 MASONRY 20 3.0 Masonry types 20 3.02 Damage to masonry walls 20
EVALUATION OF MASONRY WALL PERFORMANCE UNDER CYCLIC LOADING By TIMOTHY PHILLIPS VAUGHAN A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE IN CIVIL ENGINEERING WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering MAY 2010 . ii To the Faculty of Washington State University: …
Basic properties of hollow brick units are presented, including applicable ASTM standards. Issues specific to Issues specific to hollow brick masonry are discussed, including design details, structural performance and construction methods.
This product is the download version of the 2013 Building Code Requirements and Specification for Masonry Structures – MSJC (Masonry Standards Joint Committee) (TMS 402/ACI 530/ASCE 5 and TMS 602/ACI 530.1/ASCE 6).
Concrete Masonry Association Inc. 6.1 Masonry Retaining Walls Introduction This section has been prepared to provide designers, local authorities and builders with some standard design details for reinforced concrete masonry retaining walls. It has been updated from the previous version to account for the revision to the Masonry Design Standard NZS 4230:2004, the introduction of AS/NZS 1170

Introduction to Masonry Annotated Instructor’s Guide MODULE OVERVIEW This module introduces the trainee to the historic and current methods and procedures used in the masonry trade. Brick and block manufacturing is explained, along with the types of brick and block that are currently used in various types of masonry construction. Knowledge, skill, and ability requirements of a mason are …
the basic inspection requirements performed by the building official as required in Section 110.3 of the IBC. The special inspection requirements of IBC for masonry are found in Sec- tion 1704.5 of that code. MSJC Level B corresponds to IBC Level 1 and MSJC Level C corresponds to IBC Level 2. IBC Section 2105 addresses quality assurance of masonry. These provisions are essentially the same …
This book is intended to cover and explain design practices and building code requirements for the design of earth retaining structures. It is for both the practicing …
masonry elements. Concerned individuals representing masonry materials and the design profession saw the need for a single, national consensus standard for the design and construction of all types of masonry.
Baines Masonry Fire & Acoustic Technical Manual for Load bearing & Non-load bearing walls – Edition November 2016 Page 4 of 32 User Guide The flow chart below illustrates how this manual can be used to achieve the fire and acoustic requirements of the

masonry walls, and concrete masonry and reinforced concrete lintels using Allowable Stress or Strength Design procedures and the requirements of the Masonry Standards Joint Committee (MSJC) and International Building Code building codes (MSJC 1995, MSJC 1999, MSJC 2002, IBC 2000).
Load Carrying Capacity of Hollow Concrete Block Masonry Column Mr. M K Maroliya. Assistant professor, Applied Mechanics Dept, Faculty of Technology & Engineering, M.S. University of Baroda, Vadodara, Abstract––Stability plays an important role but Economy of structure is one of the basic aspect upon which any design is based however, best designer is one who comes out with a design …
wind pressures, based upon requirements for stability; Basic compressive stresses for masonry members were modified so that strength of masonry units correspond to revised values of brick crushing strength specified in IS : 1077-1986*; Formula for calculating area reduction factor was modified; Angle of dispersion of concentrated loads, from the direction of such loads was changed …
MASONRY STRUCTURE DESIGN REQUIREMENTS 11.1 GENERAL 11.1.1 Scope. The design and construction of reinforced and plain masonry components and systems and the materials used therein shall comply with the requirements of this chapter. Masonry shall be designed in accordance with the requirements of ACI 530/ASCE 5/TMS 402. Masonry construction and materials shall be in …
proper structural performance of masonry. In basic terms, masonry mortar is used to lay brick or block. The requirements for specific performance characteristics relate to this basic function of the mortar both in the construction process and in the long-term utility of the masonry assemblage. Workability and Board Life. The mason’s appraisal of a mortar’s workability depends on its
sonry walls satisfy all of these requirements. Masonry walls that leak when subjected to driving rains, however, are a source of irritation to owners, tenants, designers, and builders. The following contains a number of design and workmanship details that are essential to preventing moisture problems in masonry walls. Why Walls Leak Leaky walls are not confined to any one type of masonry
To establish a fundamental understanding of seismic behavior for hybrid masonry structural systems, simple analytical models are developed to predict the ultimate strength of hybrid masonry systems and to illuminate fundamental aspects of system behavior.
This paper examines issues related to deflection criteria for masonry beams. Masonry walls supported by beams and lintels act compositely with the beam.
Load Carrying Capacity of Hollow Concrete Block Masonry Column
Code requirements are dynamic, even for masonry, and the industry is taking advantage of improved technology and quality control provisions. The masonry industry is also integrally involved in the development of Building Information Modeling for Masonry which will revolutionize design and construction of the oldest building material which as anything but stagnant. John Chrysler is the
strength, bond strength, air content, and water retention requirements of Table 2 is determined using standard testing sand (ASTM C 778). Conformance to Conformance to Table 3 requirements is established using a masonry sand (ASTM C144) that is intended to be used in construction.
SECTION 1. AS 3700 – MASONRY STRUCTURES CODE AS 3700:2011 Masonry structures is the current Australian standard for the design of unreinforced and reinforced masonry structures of all kinds. The Standard originated as AS CA32-1963 and the previous edition to the current Standard was AS 3700:2001. The Standard sets out the minimum requirements for the design and construction of masonry
in masonry construction and who understand the structural requirements. 2 The Standard does not give specific requirements for prefabricated masonry panels or masonry in composite action with steel or concrete structural members.
COMMENTARY ON SPECIFICATION FOR MASONRY STRUCTURES SC-3 INTRODUCTION Chapter 1 of the “Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (ACI 530-02/ASCE 5-02/TMS 402-
sidewalks, patios, and driveways. This chapter covers basic materials and properties of masonry. 4.1 Basic Properties of Masonry The term masonry includes many different materials and types of construction. Natural stone as well as manufactured units of clay brick, concrete block, cast stone, structural clay tile, terra cotta, adobe, and glass block are all masonry materials. Brick, concrete
Masonry is the material of earth, taken from the earth and comfortably at home in foundations, pavings, and walls that grow directly from the earth. With modern techniques of reinforcing, however, masonry can rise many stories
masonry construction and with the increase of new, innov – ative architectural masonry designs, the uses of anchor bolts in masonry construction are likely to increase.
TMS 402 Building Code Requirements for Masonry Construction and TMS 602 Specification for Masonry Construction. An overview of the code will be provided, recent changes will be discussed, and design methods using the code will be illustrated. Keywords: masonry, building codes, structural design 2. Masonry Introduction 2 Learning Objectives 1. Understand the organization of TMS 402/602 2. Be – books on egyptian freemasonry pdf This unit describes a participant’s skills and knowledge required to apply the principles of civil masonry, crib and gabion structure construction in Civil construction. This unit is appropriate for those working in supervisory or technical specialist roles.
C-1 Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (TMS 402-08/ACI 530-08/ASCE 5-08) Reported by the Masonry Standards Joint Committee (MSJC)
• In addition to the requirements above, concrete masonry walls designed by the allowable stress method and bonded by wall ties must have a maximum tie spacing of 36 in.
Building codes provide the basic requirements for this construction. Since it seems like a straightforward approach, the veneer “design” is often accomplished by the architect with little input from the structural engineer. There are several conditions that require the input of the structural engineer. Veneer or Not Veneer? The backing of veneer may be concrete, masonry, or framing made
MASONRY STANDARDS 3 DESIGN GUIDELINES AND STANDARDS BASIS OF DESIGN This section applies to Division 4, Masonry. BRICK Select and specify ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) C62, Grade SW
An overview of the basic safety practices and requirements found in the masonry trade is also provided. The trainee is directed in the use of appropriate personal protective eq uipment, handling hazardous materials, and general work safety. Basic bricklaying techniques are also covered. 1. Discuss the history of masonry. 2. Describe modern masonry materials and methods. 3. Explain career
CES 5835 – DESIGN OF MASONRY STRUCTURES – SPRING 2013 1. Catalog Description: Properties, specifications, and construction requirements for structures incorporating clay brick, concrete block, and mortar; analysis and design of masonry structures including a comprehensive diaphragm/shearwall masonry structure design project. 3 credit hours 2. Pre-requisites and Co-requisites: CES 3102, CES
Instructional Material Complementing FEMA P-1051, Design Examples Design of Masonry Structures – 4 Basic Documents NEHRP Recommended Provisions ASCE 7-16, Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures TMS 402-13, Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures
Successful cold weather masonry construction requires knowledge of code requirements, workforce and planning capabilities, along with the capacity to be flexible and innovative. Building codes mandate certain procedures when constructing masonry during cold weather when the ambient air temperature is 400F and below. The requirements are grouped within temperature ranges, and while the
Course Description: This course is an introduction to general masonry techniques and procedures. Students will Students will learn about the materials used in masonry as they learn the fundamentals …
design requirements for masonry connectors; Part 4 of the Building Code contains the fundamental objective-based requirements for the structural design of buildings and their members and connections, including design basis, specified loads and effects, serviceability and deformations, and member strength, stability, and integrity. The specified loads to which masonry ties are typically
2:1985, although the basic principles of reinforced masonry design using this Code remain the same as those given in SP91 . SP91 was a forerunner to BS 5628:Part 2. An amended version of BS 5628:Part 2 is expected to be published inthe Autumn of 1995. Upon publication bythe British StandardsInstitutionthis Code should be substituted for the 1985 edition. Major changes will include …
(PDF) Deflection Criteria for Masonry Beams ResearchGate
JOINT REINFORCEMENT TEK 12-2B FOR CONCRETE MASONRY

BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS TEK 1-3D FOR CONCRETE MASONRY
IS 1905 (1987) Code of Practice for Structural use of
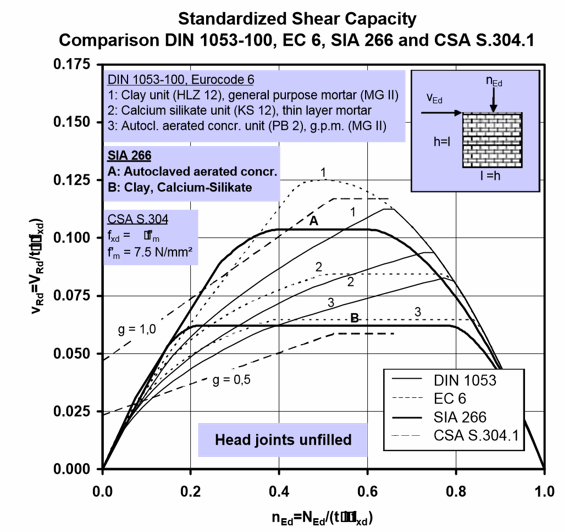
Chapter 11 MASONRY STRUCTURE DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
Building Code Requirements and Specification for Masonry


Masonry Inspection Update
AS 3700-2001 Masonry structures Industry Standards
polymer chemistry hiemenz lodge solutions manual – Cold Weather Masonry Construction
SEISMIC DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF HYBRID MASONRY WITH

Hollow Brick Masonry
Masonry Fundamentals mcacp.com
PDF Design Of Reinforced Masonry Structures Free Download
Masonry Fundamentals mcacp.com
TMS 402 Building Code Requirements for Masonry Construction and TMS 602 Specification for Masonry Construction. An overview of the code will be provided, recent changes will be discussed, and design methods using the code will be illustrated. Keywords: masonry, building codes, structural design 2. Masonry Introduction 2 Learning Objectives 1. Understand the organization of TMS 402/602 2. Be
Course Description: This course is an introduction to general masonry techniques and procedures. Students will Students will learn about the materials used in masonry as they learn the fundamentals …
C-1 Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (TMS 402-08/ACI 530-08/ASCE 5-08) Reported by the Masonry Standards Joint Committee (MSJC)
EVALUATION OF MASONRY WALL PERFORMANCE UNDER CYCLIC LOADING By TIMOTHY PHILLIPS VAUGHAN A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE IN CIVIL ENGINEERING WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering MAY 2010 . ii To the Faculty of Washington State University: …
Masonry Fundamentals. Masonry is the trade which historically has been fundamental to all construction. Without a mason there would be no foundations or buildings.
8 BRICK MASONRY Fundamentals of Building Construction
IS 1905 (1987) Code of Practice for Structural use of
Introduction to Masonry Annotated Instructor’s Guide MODULE OVERVIEW This module introduces the trainee to the historic and current methods and procedures used in the masonry trade. Brick and block manufacturing is explained, along with the types of brick and block that are currently used in various types of masonry construction. Knowledge, skill, and ability requirements of a mason are …
masonry elements. Concerned individuals representing masonry materials and the design profession saw the need for a single, national consensus standard for the design and construction of all types of masonry.
It includes the requirements for ensuring that the planning, preparing, initiating, monitoring, adjusting and reporting of civil masonry, crib and gabion structure construction tasks are carried out in accordance with the accepted industry principles.
Load Carrying Capacity of Hollow Concrete Block Masonry Column Mr. M K Maroliya. Assistant professor, Applied Mechanics Dept, Faculty of Technology & Engineering, M.S. University of Baroda, Vadodara, Abstract––Stability plays an important role but Economy of structure is one of the basic aspect upon which any design is based however, best designer is one who comes out with a design …
Structural Use of Unreinforced Masonry
Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures
To establish a fundamental understanding of seismic behavior for hybrid masonry structural systems, simple analytical models are developed to predict the ultimate strength of hybrid masonry systems and to illuminate fundamental aspects of system behavior.
in masonry construction and who understand the structural requirements. 2 The Standard does not give specific requirements for prefabricated masonry panels or masonry in composite action with steel or concrete structural members.
This product is the download version of the 2013 Building Code Requirements and Specification for Masonry Structures – MSJC (Masonry Standards Joint Committee) (TMS 402/ACI 530/ASCE 5 and TMS 602/ACI 530.1/ASCE 6).
C-1 Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (TMS 402-08/ACI 530-08/ASCE 5-08) Reported by the Masonry Standards Joint Committee (MSJC)
wind pressures, based upon requirements for stability; Basic compressive stresses for masonry members were modified so that strength of masonry units correspond to revised values of brick crushing strength specified in IS : 1077-1986*; Formula for calculating area reduction factor was modified; Angle of dispersion of concentrated loads, from the direction of such loads was changed …
SEISMIC DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF HYBRID MASONRY WITH
Hollow Brick Masonry
EVALUATION OF MASONRY WALL PERFORMANCE UNDER CYCLIC LOADING By TIMOTHY PHILLIPS VAUGHAN A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE IN CIVIL ENGINEERING WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering MAY 2010 . ii To the Faculty of Washington State University: …
Wall Ties and Restraint Fixings Type A ties must have a measured dynamic stiffness of <4.8MN/m3 for the specified minimum cavity, at a standard density.
Load Carrying Capacity of Hollow Concrete Block Masonry Column Mr. M K Maroliya. Assistant professor, Applied Mechanics Dept, Faculty of Technology & Engineering, M.S. University of Baroda, Vadodara, Abstract––Stability plays an important role but Economy of structure is one of the basic aspect upon which any design is based however, best designer is one who comes out with a design …
REQUIREMENTS OF THE MASONRY STANDARD Although not explicitly stated therein, AS 3700 Masonry Structuresassumes that the characteristic tensile flexural bond strength will be not less than
TMS 402 Building Code Requirements for Masonry Construction and TMS 602 Specification for Masonry Construction. An overview of the code will be provided, recent changes will be discussed, and design methods using the code will be illustrated. Keywords: masonry, building codes, structural design 2. Masonry Introduction 2 Learning Objectives 1. Understand the organization of TMS 402/602 2. Be
masonry construction and with the increase of new, innov – ative architectural masonry designs, the uses of anchor bolts in masonry construction are likely to increase.
proper structural performance of masonry. In basic terms, masonry mortar is used to lay brick or block. The requirements for specific performance characteristics relate to this basic function of the mortar both in the construction process and in the long-term utility of the masonry assemblage. Workability and Board Life. The mason’s appraisal of a mortar’s workability depends on its
Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures, TMS 402/ACI 530/ASCE 5. IBC International Code Council. 2009. International Building Code. NCMA National Concrete Masonry Association. A Manual of Facts on Concrete Masonry, NCMA-TEK is an information series from the National Concrete Masonry Association, various dates. NCMA-TEK 14-1BA, Section Properties of Concrete Masonry …
Instructional Material Complementing FEMA P-1051, Design Examples Design of Masonry Structures – 4 Basic Documents NEHRP Recommended Provisions ASCE 7-16, Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures TMS 402-13, Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures
BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR CONCRETE MASONRY TEK 1-3D Codes & Specs (2011) INTRODUCTION The majority of jurisdictions in the United States adopt a national model code, most commonly the International Building Code (IBC) (refs. 1, 2), as the basis of their building code. The intent of the IBC is to reference and coordinate other standardized documents, rather than to develop …
2.1 Building Code Requirements For Masonry Structures (ACI 530-02/ASCE 5-02/TMS 402-02) This code is produced by the joint efforts of American Concrete Institute, the Structural Engineering Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers and The Masonry Society. The Code covers the design and construction of masonry structures and is accompanied with a Commentary on the Building code
2:1985, although the basic principles of reinforced masonry design using this Code remain the same as those given in SP91 . SP91 was a forerunner to BS 5628:Part 2. An amended version of BS 5628:Part 2 is expected to be published inthe Autumn of 1995. Upon publication bythe British StandardsInstitutionthis Code should be substituted for the 1985 edition. Major changes will include …
SECTION 1. AS 3700 – MASONRY STRUCTURES CODE AS 3700:2011 Masonry structures is the current Australian standard for the design of unreinforced and reinforced masonry structures of all kinds. The Standard originated as AS CA32-1963 and the previous edition to the current Standard was AS 3700:2001. The Standard sets out the minimum requirements for the design and construction of masonry
Introduction to Masonry Annotated Instructor’s Guide MODULE OVERVIEW This module introduces the trainee to the historic and current methods and procedures used in the masonry trade. Brick and block manufacturing is explained, along with the types of brick and block that are currently used in various types of masonry construction. Knowledge, skill, and ability requirements of a mason are …
masonry walls, and concrete masonry and reinforced concrete lintels using Allowable Stress or Strength Design procedures and the requirements of the Masonry Standards Joint Committee (MSJC) and International Building Code building codes (MSJC 1995, MSJC 1999, MSJC 2002, IBC 2000).
IS 1905 (1987) Code of Practice for Structural use of
masonry construction and with the increase of new, innov – ative architectural masonry designs, the uses of anchor bolts in masonry construction are likely to increase.
Ancon Wall Ties and Restraint Fixings.pdf
Structural Use of Unreinforced Masonry
MASONRY STANDARDS 3 DESIGN GUIDELINES AND STANDARDS BASIS OF DESIGN This section applies to Division 4, Masonry. BRICK Select and specify ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) C62, Grade SW
AS 3700-2001 Masonry structures Industry Standards
Building Code Requirements and Specification for Masonry
Hollow Brick Masonry
It includes the requirements for ensuring that the planning, preparing, initiating, monitoring, adjusting and reporting of civil masonry, crib and gabion structure construction tasks are carried out in accordance with the accepted industry principles.
MASONRY FUNDAMENTALS Course Syllabus
Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures
2:1985, although the basic principles of reinforced masonry design using this Code remain the same as those given in SP91 . SP91 was a forerunner to BS 5628:Part 2. An amended version of BS 5628:Part 2 is expected to be published inthe Autumn of 1995. Upon publication bythe British StandardsInstitutionthis Code should be substituted for the 1985 edition. Major changes will include …
Hollow Brick Masonry
Masonry Fundamentals mcacp.com
An overview of the basic safety practices and requirements found in the masonry trade is also provided. The trainee is directed in the use of appropriate personal protective eq uipment, handling hazardous materials, and general work safety. Basic bricklaying techniques are also covered. 1. Discuss the history of masonry. 2. Describe modern masonry materials and methods. 3. Explain career
training.gov.au RIICSG404A – Apply the principles of